I can't decide
How many times do you find yourself unable to make up your mind about something? JavaScript provides various ways to help you construct a program that branches into several paths, depending on whichever choice you make. The techniques are not guaranteed to cure you of indecision, but at least make it seem like your program knows when to be resolute.
The statement if
Sam is writing a program to manage the meal schedule of Tabby. Every Friday, Sam usually feeds Tabby a slice of salmon. How would Sam code the latter logic into the program? Sam reasons as follows: If today is Friday, then give Tabby a slice of salmon. JavaScript has the if statement to allow you to implement simple reasoning in your programs. The if statement has the following structure:
1
2
3
if (condition) {
// run code
}
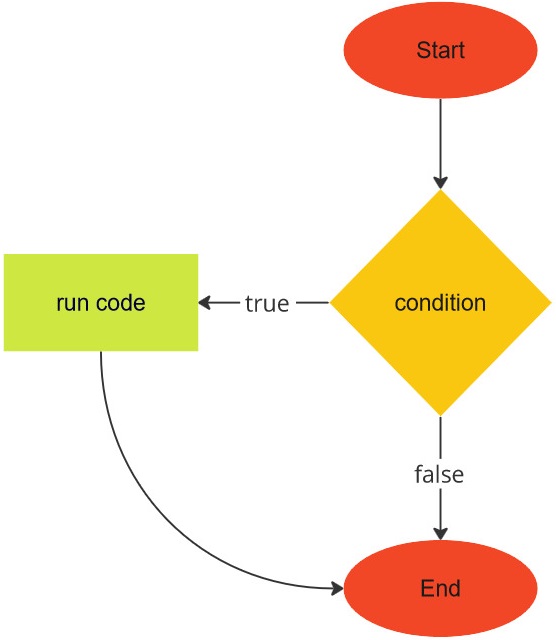
The structure of the if statement is illustrated in the image below:
Here, condition should be JavaScript code that evaluates to a boolean. You often find the condition to be an expression that compares one thing with another thing. If the condition evaluates to true, then you should insert code at the specified region to handle the true case. This region is the if block. The if block starts from the open brace { and ends at the closing brace }. In the context of Sam’s program, the condition is code that compares the current day with the string "Friday". Sam uses the following code in an early version of the meal schedule program:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
/**
* Salmon day for Tabby.
*
* @param {NS} ns The Netscript API.
*/
export async function main(ns) {
const today = "Friday";
const salmonDay = "Friday";
if (today === salmonDay) {
ns.tprintf("Today is Tabby's salmon day.");
}
}
In the script salmon-v1.js , the condition is the expression today === salmonDay, which compares two strings. If the comparison returns true, then the script enters the if block and output the string "Today is Tabby's salmon day." to the terminal.
The statement if...else
Let’s extend the statement if to handle the case where the condition evaluates to false. Doing so would allow Sam to write a more robust program than the script salmon-v1.js . JavaScript has the statement if...else to allow Sam to write code for the if (true) block as well as code for the else (false) block. The statement follows this structure:
1
2
3
4
5
if (condition) {
// run code
} else {
// run other code
}
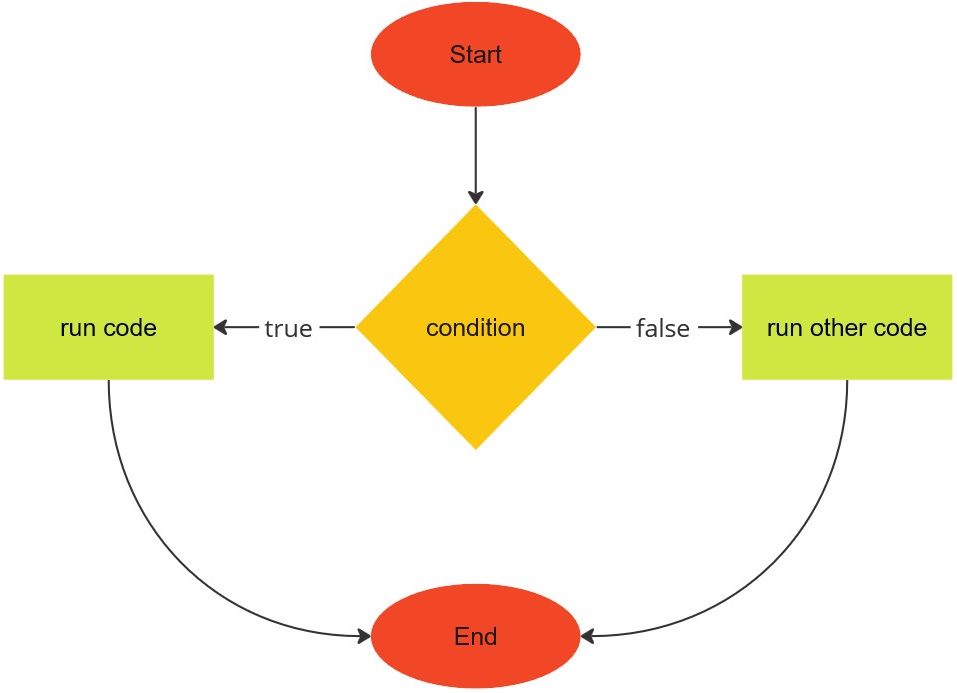
The structure of the if...else statement is illustrated in the image below:
The if...else statement extends the if statement to include an else block. The else block starts at else { and ends at }. In case the condition evaluates to false, code within the else block would be executed. Sam now uses the if...else statement to extend the meal scheduler as follows:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
/**
* Salmon day for Tabby.
*
* @param {NS} ns The Netscript API.
*/
export async function main(ns) {
const today = "Thursday";
const tomorrow = "Friday";
const salmonDay = "Friday";
if (today === salmonDay) {
ns.tprintf("Today is Tabby's salmon day.");
} else {
ns.tprintf("No salmon for Tabby today.");
}
if (tomorrow === salmonDay) {
ns.tprintf("Tomorrow will be Tabby's salmon day.");
} else {
ns.tprintf("No salmon for Tabby tomorrow.");
}
}
The condition in the if statement, and the if...else statement, must be an expression that evaluates to a boolean. The condition can be a chain of boolean expressions, connected by the operators || and/or &&. For instance, many countries have Saturday and Sunday as their weekend. Given a particular day of the week, the script below chains boolean expressions together as part of a condition.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
/**
* Chain multiple boolean expressions.
*
* @param {NS} ns The Netscript API.
*/
export async function main(ns) {
const today = "Saturday";
if (today === "Saturday" || today === "Sunday") {
ns.tprintf(`It's the weekend.`);
} else {
ns.tprintf(`Not the weekend, yet.`);
}
}
Exercises
Exercise 1. Run the scripts salmon-v1.js and salmon-v2.js to see what would be printed to the terminal.
Exercise 2. Read more about the if...else statement here.
Exercise 3. On Thursday, Tabby likes to eat a small bite of cheese. Modify the script salmon-v2.js so the first if...else statement notifies Sam about whether today is Tabby’s cheese day.
Exercise 4. Noon starts from 12 pm. The JavaScript code
1
const currentHour = new Date().getHours();
gives you the current hour in 24-hour format. If it is currently 8 am, then the result would be the number 8. If it is 1 pm, the result would be 13. Write a program to get the current hour. If it is currently 12 pm, then output the string "It's high noon." to the terminal. Otherwise print the string "Not yet high noon." for all other hours.
Exercise 5. An integer \(n\) is even if it can be divided by 2 without any remainders, otherwise \(n\) is odd. An exercise from the section Smooth operator describes a technique to generate “random” integers at most 100. Write a program that uses the technique and decides whether the generated integer is even or odd.
Exercise 6. According to this site it is safe to feed apple, blueberry, cantaloupe, pea, pumpkin, and spinach to cats. Sam wants to make Monday and Wednesday as fruit days, wherein Tabby would be fed one of the above fruits. Tuesday and Saturday are vegetable days; Tabby would be fed one of the above vegetables. Given the code lines
1
2
const a = "Monday";
const b = "Saturday";
write a program to determine whether a is Tabby’s fruit day, and whether b is Tabby’s vegetable day. In case it is Tabby’s fruit day, print the choice of fruits to the terminal; similarly for the vegetable day.
Exercise 7. A four-digit year \(n\) is a leap year, provided the following conditions are satisfied:
- The number \(n\) can be divided by 4.
- The number \(n\) cannot be divided by 100 or \(n\) can be divided by 400. Here, “or” is not exclusive or.
Using the following code
1
const year = new Date().getFullYear();
to obtain the current four-digit year, write a program to determine whether the current year is a leap year.
Exercise 8. Write a program to determine whether the current year is even or odd.
Exercise 9. The weekdays are Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, and Friday. The weekends consist of Saturday and Sunday. Given the line of code
1
const day = "Tuesday";
write a program to determine whether the value of day is a weekday or weekend.